21 min read • Financial services
From micro-saving to big impact
The world of embedded savings


Executive Summary
AN UNDERESTIMATED RESOURCE
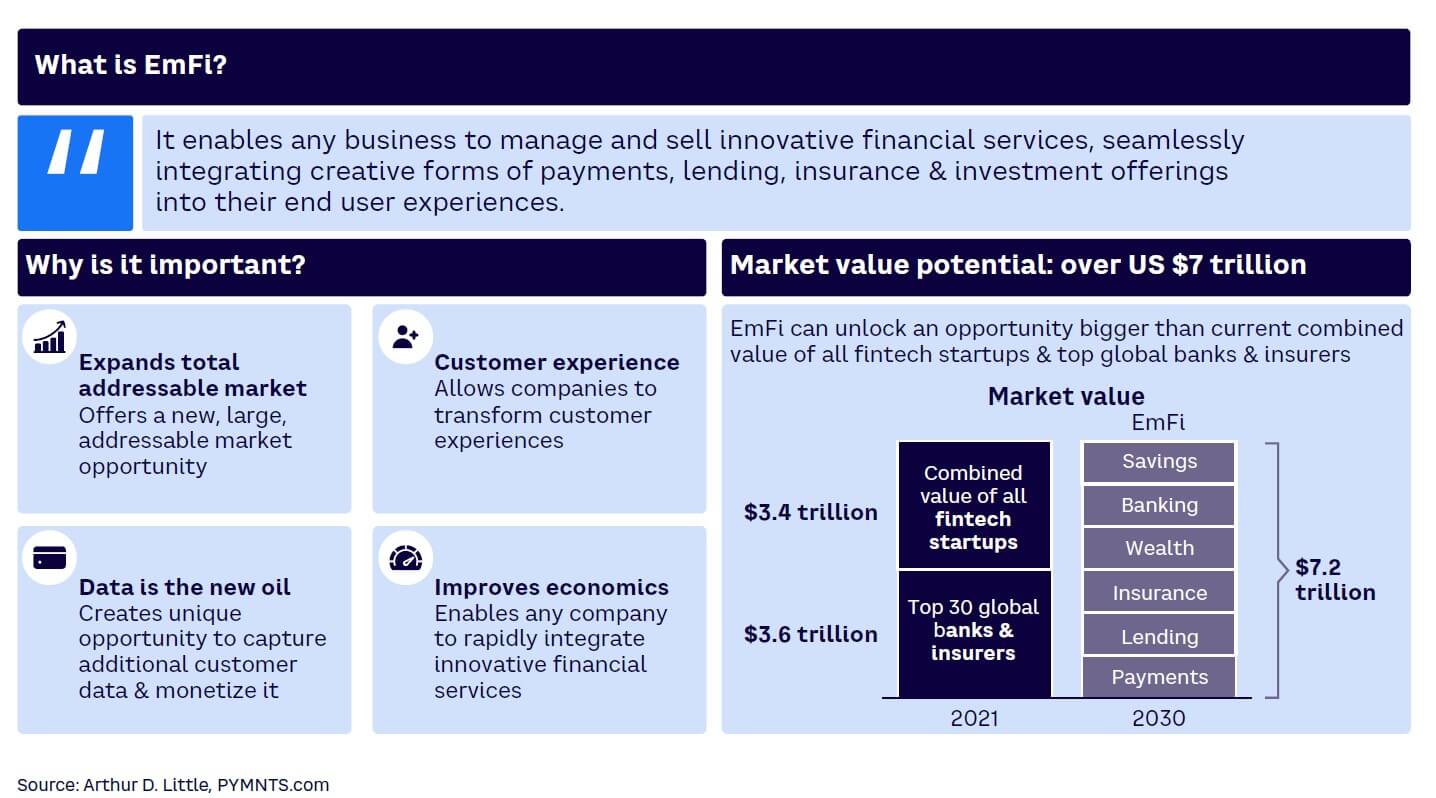
Embedded finance (EmFi) arguably has been the most hyped financial technology topic of the past two years. Its rise has forced traditional finance to take a back seat to make way for a more integrated and seamless customer experience. The EmFi market size and its many components, including payments, lending, savings, insurance, and investments, is estimated to reach US $7.2 trillion by 2026.
While EmFi’s focus is often on payments and lending, there is a lesser-known side of the trend: embedded savings. Despite the possibilities, which are wide-ranging and largely untapped, embedded savings has yet to receive its share of recognition and attention. In this Report, we aim to shed light on the importance of embedded savings and why it deserves more consideration in the context of EmFi. We will examine:
-
How embedded savings differs from other forms of EmFi.
-
Categories of embedded savings products.
-
Benefits of incorporating embedded savings into an EmFi strategy.
-
Real-life use cases that already exist around the world.
-
Criteria for selecting the ideal technology partner.
1
UNCOVERING THE POTENTIAL OF EMBEDDED SAVINGS
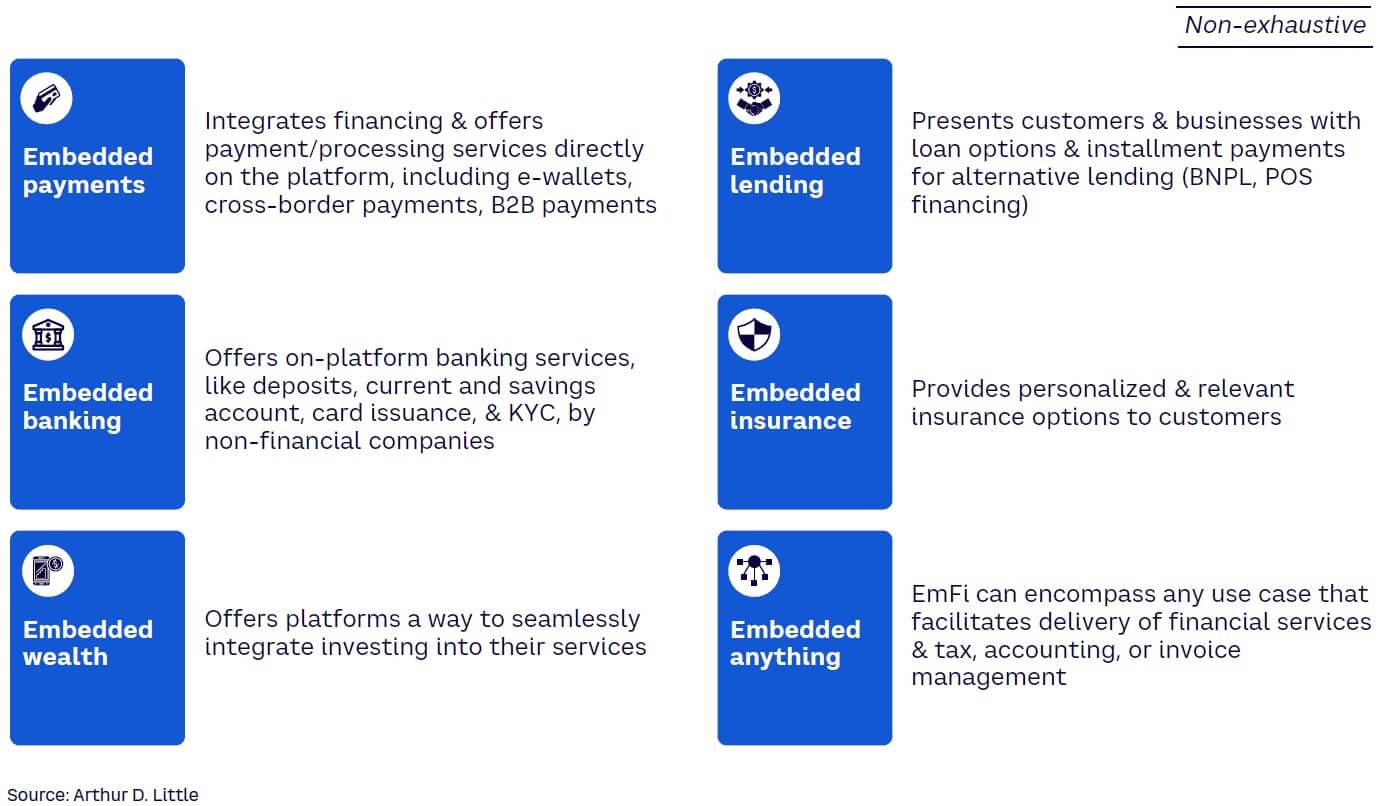
EmFi is essentially the placement of a financial product in a nonfinancial customer experience, journey, or platform (see Figure 1). This concept is transforming the way customers and businesses approach financial services (see Figure 2). The following EmFi components have already gained traction:
-
Embedded banking — the integration of banking services into nonfinancial products and services. This integration can take various forms, such as card issuance or “know your customer” (KYC) verification integrated into a mobile app or online platform.
-
Embedded payments — the integration of payment services into nonfinancial products and services. Enabling mobile payments within a ride-sharing app or allowing customers to pay for goods and services through a social media platform are two examples.
-
Embedded lending — the integration of lending services into nonfinancial products and services. Like embedded payments, this service can take different forms, such as financing options for products or services, or loans within a bundled package. For example, an automobile dealership may offer financing options for customers looking to purchase a car by including lending services in the dealership’s overall offerings.
-
Embedded wealth — the integration of wealth management services into nonfinancial products and services. This can be accomplished by providing access to investment options, retirement savings plans, and other financial products embedded as part of a broader offering. Wealth management firms aim to offer customers added convenience and value while expanding their revenue streams and reaching new markets.
-
Embedded insurance — the integration of insurance services within nonfinancial products and services. Adding insurance coverage to a product or service or offering insurance products as an additional benefit to customers are two of the many possibilities.
-
Embedded anything — the integration of financial tools for taxes, accounting, and invoicing into nonfinancial products and services. Examples include embedding tax-preparation services into accounting software or integrating invoicing services into an e-commerce platform.
One aspect of EmFi that remains relatively unexplored is embedded savings: the integration of savings and investment services within nonfinancial products and services. Embedded savings enables customers to easily save small amounts of money — or save and invest — as part of their everyday transactions. The concept of embedded savings is relatively new, and many people are not yet aware of its benefits and applications. Generally, the conversation around EmFi has largely centered on services that drive revenue and growth for businesses, like payments and lending, rather than savings, which promote financial wellness and stability for individuals. However, embedded savings has the potential to drive revenue and growth for the customer, embedder, and provider.
While the established elements of EmFi play a significant role in shaping the future of finance, embedded savings arguably has the most potential to meaningfully change the lives of customers and businesses by making it easier and more convenient to save for a rainy day, a specific future need, or long-term investments.
2
WHY TALK ABOUT EMBEDDED SAVINGS NOW?
Savings form a crucial foundation for financial activities, including lending, liquidity provision, and investment. A reduction in deposits and savings might force a bank to sell assets or seek other ways to create liquidity. Failing to attract deposits can have dire repercussions on the bottom line, as shown by the failure of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in March 2023. Banks do not always view savings as a core aspect of their business strategy, so they may not prioritize promoting this product. Instead, banks will prioritize lending and investment activities, which generate more revenue for them. Savings may be viewed as a peripheral activity that does not align with their primary objectives, and it may not generate enough revenue for banks to justify the cost of managing the accounts. As a result, banks may not be promoting savings as much as they could, even though these accounts are necessary to financial wellness and can help attract and retain customers.
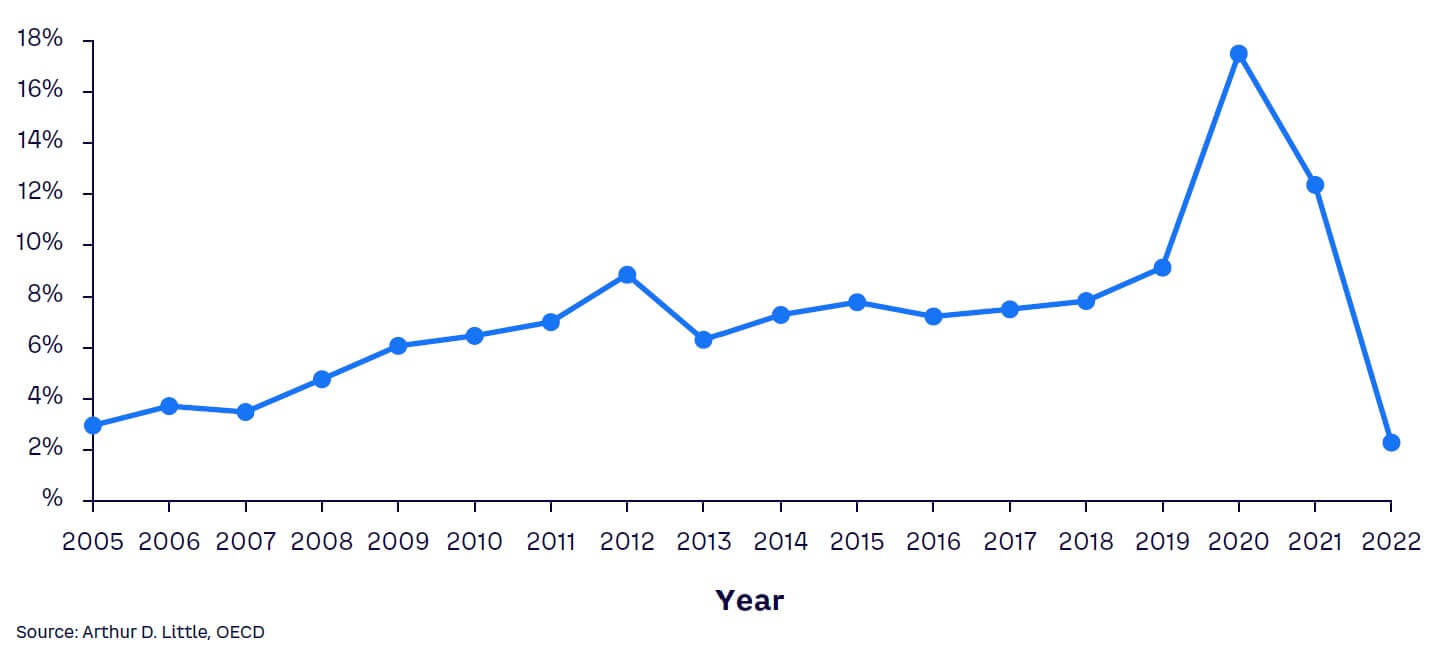
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted many aspects of life, including individuals’ saving habits. The personal savings rate — how much money people save compared to their total disposable income — spiked during the pandemic. In 2020, according to Moody’s, the estimated personal savings rate in the US averaged 9%. This was attributed to several factors, including lower expenditures on items such as transport and entertainment, reduced opportunities to spend money due to lockdowns and other restrictions, and for some, additional income from government stimulus and support programs.
By October 2022, the surge in living costs and inflation rates that followed the pandemic quickly reversed the saving trend, causing a drop in the personal savings rate to 2.3% (see Figure 3). However, the rising inflation trend ended near-zero and sub-zero interest rates. The interest rates on savings accounts are tracking the base rates and rising for the first time since 2007–2008, with interest rates of 4%-5% becoming attainable in most localities. In March 2023, four different providers were offering rates over 4% in the UK, according to Bankrate.com.
As prices and interest rates payable on savings are rising, it is not surprising that people have become fussier about their banking products and are open to switching providers in the hopes of beating inflation through their savings. Meeting customers’ changing needs has increased demand for innovative solutions to help individuals save and manage their money. Embedded savings is flexible and adaptable, and it should be at the forefront as it offers unique, effective solutions for individuals to automate their savings and achieve their financial goals.
The climate is favorable for developing and launching embedded savings products thanks to both positive and negative undercurrents that impact individuals, businesses, and the world:
-
Changing consumer behavior. With a growing awareness of the importance of personal finance and saving, customers are seeking solutions that can help them achieve their financial goals with ease. Embedded savings can meet their needs by providing an effortless and automated way to save. It aligns with the idea of holistic wellness, which encompasses physical, mental, and financial well-being, by offering an easy and convenient way to improve one’s financial wellness without sacrificing time and energy.
-
Technology breakthroughs. The availability of infrastructure like banking as a service (BaaS) and open banking has enabled the seamless integration of savings into daily routines, including online shopping, mobile banking, and payments. This allows customers to save unconsciously and presents opportunities for businesses to embed finance solutions in their platforms, which makes saving more convenient and accessible for individuals. Open banking gives customers access to their banking information and services through third-party providers, enabling greater flexibility and choice. These technological advancements create new opportunities for businesses to offer embedded savings solutions and meet the growing demand for convenient savings options.
-
Untapped market potential. The rise of fintechs and new financial platforms has made it easier for customers to access financial products and services and enjoy better user experiences. These new entrants have successfully attracted large numbers of customers, including younger and tech-savvy ones. By integrating savings and investment options seamlessly into existing platforms, embedded savings solutions can provide a more holistic approach to financial management that is advantageous for customers, which can help drive mainstream adoption of these solutions and lead to a new era of financial wellness.
-
Economic volatility. Across the globe, the average 30-year-old has witnessed several major financial crises, including the 2008 housing bubble, the 2012 European debt crises, hyperinflation across developing world economies, and the crypto rise and crash. These economic fluctuations have left many customers feeling uncertain about their financial future. Embedded savings can address their concerns and impart a sense of stability by helping them save automatically, regardless of the state of the economy. Customers build a cushion for unpredictable times, maintain their purchasing power, and plan for the future with greater confidence.
-
Declining customer trust. In recent years, trust in traditional banks has been declining, and many customers are turning to alternative brands for their financial needs. For example, Apple has become a major player in the financial industry, starting with facilitation of payments through Apple Pay, followed by issuance of Apple Card with Goldman Sachs that incentivizes its users to transact and engage with the card, and most recently Apple rolled out high-yield savings accounts for its Apple Card users. According to FDIC data, more than 85% of US banks have less than $1 billion in total assets, which suggests that customers are increasingly seeking out nontraditional financial options. The shift in customer behavior presents both a challenge and an opportunity for traditional banks. Banks can maximize emerging solutions like embedded savings to meet the evolving needs of their customers and build long-term trust and loyalty.
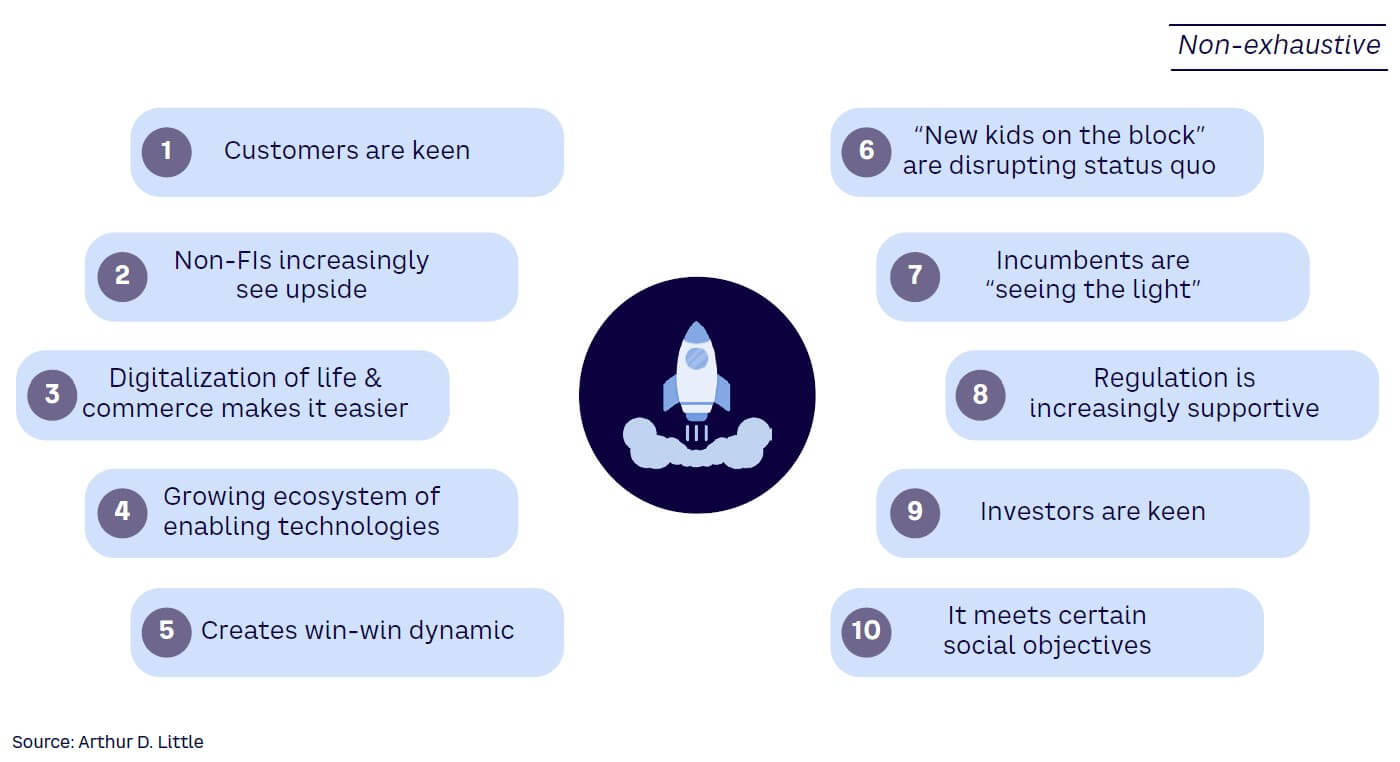
These factors, along with the drivers shown in Figure 4, highlight why now is the perfect time for businesses to build solutions around embedded savings, which make it easier for individuals to achieve their financial goals.
3
EXPLORING THE COMPONENTS OF EMBEDDED SAVINGS
According to a report by the Financial Health Network, people who use automatic savings tools save on average $217 more per month (equivalent to 7% of an income of $3,500) than those who do not.
Because embedded savings continues to gain momentum, it is essential to understand its fundamentals. It encompasses a wide array of products and services, from traditional savings accounts to cutting-edge, micro-saving solutions that allow customers to regularly save small amounts of money. Let’s delve into the various types of embedded savings and micro-savings and highlight some of the industry leaders that have successfully implemented these state-of-the-art solutions:
-
Automated savings. This mechanism allows individuals to put money aside without having to actively think about it or make manual transfers. The basis is simple: make saving as effortless as possible. Automating the process may make customers less likely to change or cancel it, and more likely to stick to it. One example is Astra Finance, a US-based fintech, which allows its customers to set up automated transfers between their different accounts.
-
Round-up savings. This type of micro-saving rounds up transactions to the nearest whole unit and automatically transfers the difference into a savings account. Rounding up is designed to help individuals save small amounts of money regularly; they can accumulate a balance without even realizing it. It makes saving money effortless and convenient. Jar, a fintech based in India, offers its users the opportunity to round up their purchases and invest the amount in safe commodities such as gold.
-
Social savings. As the name suggests, this approach brings a group of individuals together to save toward a selected common financial goal, harnessing the power of community and peer pressure to encourage people to save more. By pooling their resources, individuals can achieve their financial goals more easily, as they are able to save more than they would be able to on their own. Nigerian fintech Cowrywise leverages the passion fans have for sports to encourage saving. Customers can use the Cowrywise platform to link their savings account to their favorite football team. Every time the team scores, Cowrywise automatically transfers a monetary incentive into the customer’s savings account.
-
Behavioral savings. This tactic leverages psychology and behavior-change theories to encourage customers to save more, using gamification, social comparison, and nudging strategies to help customers develop healthy savings habits and reach their financial goals. For example, US-based mobile app Qapital enables users to customize their savings using the If This Then That (IFTTT) rule. Users can identify specific behaviors, such as checking into a gym or buying coffee, and set up automated transfers for their accounts that are carried out in conjunction with those behaviors.
-
Save now, buy later (SNBL). This creative new model started in Africa and allows customers to save for desired items in small increments, optimize their cash flow, lock in deals, and avoid borrowing (i.e., buy now, pay later). An SNBL provider teams up with retailers to offer the service to the customer at checkout. As customers hit milestones on the way to saving for the item they want, they earn cash back and rewards from the retailer. FlexPay Technologies, Tunzaa Fintech, and CDcare offer SNBL.
The market is now witnessing the rise of specialized companies dedicated to seamlessly embedding solutions such as those described above into businesses’ journeys, providing customers with a new realm of opportunities to achieve financial stability and growth.
4
UNLOCKING THE BENEFITS OF MICRO-SAVING
As the trend of micro-saving gains momentum and the number of providers offering embedded savings solutions increases, it becomes evident that this field is ripe for imagination. Merging micro-saving with a business’s other offerings can improve the bottom line for both the business and the customers. Some potential benefits are:
-
Increased customer engagement. Offering micro-saving features can help to increase customer engagement and foster loyalty, as customers are able to save and manage their finances in a way that is convenient and incorporated into their daily lives.
-
Improved financial wellness. By providing customers with easy and convenient ways to save, businesses can help improve customers’ financial wellness and contribute to a more financially stable community.
-
Enhanced customer experience. Adding micro-saving features to a business’s products can create a more seamless and enjoyable customer experience and make it easier for customers to achieve their financial goals and feel more in control of their finances.
-
Increased brand differentiation. Offering options for micro-saving can set a business apart from its competitors and position it as a leader in financial innovation, which could attract new customers and increase brand recognition.
-
Increased revenue. Providing customers with a valuable service that supports their financial goals will benefit businesses as well by resulting in new revenue streams and increasing their customer base, and ultimately leading to increased profitability.
-
Improved financial literacy. Offering micro-saving features can help to improve financial literacy by showing customers the different ways they can harness their spending and encouraging them to make informed financial decisions, which can have a positive impact on their financial futures.
Now that we have a clear understanding of micro-saving, its various components, and the potential benefits it can bring businesses and customers, it’s time to explore the specifics of implementing a strategy.
A recent study from the UK found a significant increase in savings participation from the integration of automated savings into payroll, which soared from a mere 1.3% to an impressive 52.6%. This highlights the effectiveness of embedded savings in encouraging individuals to save and take control of their financial well-being. How can businesses effectively incorporate micro-saving into their offerings and maximize this innovative financial service for the benefit of their customers and their brand?
5
EMBEDDED SAVINGS USE CASES — FROM LUXURY GOODS TO UTILITIES
Here are several examples of how embedded savings and micro-savings can be folded into businesses across different industries:
-
Luxury goods. Many people are interested in purchasing luxury items, but it can be a challenging goal to achieve. Micro-saving offers a solution by enabling customers to set aside small amounts of money over time. For instance, a customer could decide to save for a luxury bag and have a designated amount automatically transferred into their savings account each month. This would increase the chance of success as saving would become a regular and automatic part of their routine.
-
Retail. Retailers can enhance customer loyalty and drive repeat business through a micro-savings program. For example, a clothing retailer can offer a program where customers can automatically set aside a small amount each time they make a purchase. This allows customers to save for a desired item and encourages them to continue shopping at that store. In this way, the micro-saving tool creates loyal, returning customers.
-
Travel. There are clear applications for the travel industry. Many individuals aspire to travel, but the expense is often too high. Travel companies can support their customers by providing micro-savings plans to fund their travel dreams. Implementing a program where a small amount is automatically saved from each purchase or booking can assist customers in saving for their future travels and benefit the travel company by boosting customer loyalty and generating repeat business.
-
Health and wellness. A health and wellness company can introduce a savings plan to encourage customers to lead healthier lifestyles through exercise and eating well by offering incentives for reaching predetermined objectives. This assists customers in saving during their journey toward their health and wellness goals while reinforcing positive habits, leading to a healthier lifestyle. To enhance customer engagement, a gym could implement a savings program that rewards members who meet their fitness goals and penalizes those who don’t by adjusting the interest or reward paid into the savings account based on a customer’s behaviors.
-
Home and car ownership. Real estate companies can provide a savings program aimed at helping customers accumulate funds for a down payment. This program can be seamlessly integrated with the company’s other services, such as mortgage brokerage or property management, to support customers in achieving their homeownership aspirations. Car dealerships can offer similar programs for customers who wish to save for a car purchase by integrating their financing and insurance services. In such scenarios, customers could be offered discounts in buying the adjacent services (i.e., insurance and services) if the payment toward those services is made through the savings program. This not only supports customers in reaching their goals but also strengthens customer loyalty, increases customer conversion, allows the business to close more sales, and prevents the loss of potential customers.
-
Retirement savings. Financial services and insurance companies can offer micro-savings plans for retirement saving. The plan could be integrated into the company’s existing products, such as investment services, and would facilitate saving small amounts and managing retirement funds over time. By automating the process, customers can consistently contribute to their retirement savings goals and gradually grow their nest egg. The convenience and simplicity of this micro-savings plan can encourage customers to prioritize retirement saving and achieve their financial goals.
-
Energy and utilities. A utility provider can encourage customers to reduce their energy consumption by introducing a micro-savings feature. Whenever the customer saves energy — through using energy-efficient appliances or turning off unneeded lights, for example — the provider will automatically place the difference between the energy saved and their average usage into a savings account. This creates a tangible incentive for customers to conserve energy; they will see their savings grow with each effort to reduce their energy usage. The utility provider benefits as well, as it can reduce the demand for energy and lower its costs. The provider can also earn revenue from the program, creating a mutually beneficial solution for both parties.
These are just a few examples of how micro-saving can be incorporated into different businesses to improve customer engagement, enhance the customer experience, and achieve specific financial goals for businesses and individuals.
6
CHOOSING THE RIGHT TECHNOLOGY PARTNER
An embedded savings program can help a business support its objectives while significantly contributing to its customers’ financial wellness and stability. The right technology partner can offer customization options tailored to the business’s unique requirements and oversee a smooth and successful implementation. To ensure compatibility between a business and a technology partner, look for a partner that offers the following features:
-
Automated customer savings. Essential to any embedded savings program, this feature streamlines the savings process for customers, making it effortless and stress-free. By automating, a business can help its customers keep track of their financial progress and empower them to achieve their financial goals. These include recurrent savings, round-up savings, behavioral savings, and others.
-
Regulation-compliant value storage. It is crucial to ensure that the stored value, which is the balance needed for future transactions, complies with relevant regulations to protect the customers’ savings. This ensures the security and protection of their funds, which helps build trust in the business and enhances the overall customer experience. A deep understanding of the regulations for issuing stored value is critical to effectively operate any embedded savings program and provide peace of mind for customers.
-
Goal-based savings. This option helps customers envision their objectives and build their savings accordingly by enabling them to set a target and track their progress. Customers gain a clear vision of their financial future, which keeps them motivated to save.
-
Bank accounts with data integration. A comprehensive view of a customer’s financial situation and spending habits is essential for effective savings. Bank accounts with data integration offer valuable insights into customer finances. This integration supports informed financial decision-making and drives additional savings to help customers reach their financial goals while giving the business a better understanding of its customers and their financial needs.
Embedded savings is starting to gain more relevance and popularity as more fintechs shift their focus to this underutilized segment of EmFi, and businesses are taking note of the results. This is a good time for businesses to exploit the developing interest in and options for embedded savings to seek out the right partnership.
By collaborating with a fintech provider that offers the features it needs, a business can ensure that its embedded savings program is effective, efficient, and customer-centric. A strong collaboration supports the business’s goals and promotes financial wellness and stability for its customers.
There are several fintechs helping businesses develop their ideal embeddable saving programs; these include global companies like Meniga, Dreams Technology, and regional players like Coinscrap in Spain and TWIG in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). Each offers comprehensive platforms that provide what is needed to implement an effective embedded savings program. The accompanying case studies represent trailblazing ideas that utilize EmFi to bring value and revenue to the fintech industry.
Case studies
Acorns
Acorns is an Irvine, California, USA-based fintech founded in 2012. The company offers a mobile app that enables users to invest their spare change from everyday purchases into a diversified portfolio of exchange-traded funds (ETFs). The company’s unique approach to savings has been a game changer in the financial industry, allowing people to invest small increments with ease. With over 8 million users, Acorns has gained significant recognition for its innovative platform, which also includes personalized investment advice, retirement savings accounts, and educational tools to help users manage their finances effectively.
Qapital
Qapital is headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, and operates in the US and Canada. The company was founded in 2012 by a group of financial and technology experts whose goal was to provide a mobile-based platform to help people save money more easily. Qapital has earned attention for its creative approach to savings. Its mobile app offers unique tools designed to help users personalize their experience, like the “Rules” feature, which guides the creation of behavior-based savings criteria, including the use of IFTTT, which work automatically to save money based on specific actions or events.
N26
N26 is a fintech company operating in Europe and the US. Founded in 2013, it provides mobile-based banking services with a user-centered approach to design. Its commitment to providing modern and convenient banking services has made it a popular choice for customers looking for a hassle-free banking experience. N26 offers various saving automations embedded in its application, such as automated transfers between accounts, with a feature that rounds each transaction up to the nearest euro or dollar and automatically saves the difference. N26’s features make saving a seamless part of everyday life, helping users achieve their financial goals.
Jar
Founded in 2021, Jar is a fintech company operating in India. Jar provides a mobile-based savings platform that enables users to link their bank accounts and automatically invest spare change from each transaction in gold. Saving through gold investing is an attractive option for people looking to diversify their investment portfolio and protect their savings against market fluctuations. By offering a savings solution that allows users to invest in gold, Jar is tapping into a cultural preference and providing a convenient way for people to invest in this valuable asset.
TWIG
TWIG is a UAE-based fintech founded in 2021. Originally a direct-to-customer mobile app, TWIG’s platform offers micro-saving functionalities to drive additional savings such as rounding up, goal-based savings, and artificial intelligence (AI)-based budgeting. The company’s product-driven approach prioritizes customer and user experience. With its expansion to include B2B2C solutions and its deep understanding of the Middle East and North Africa’s (MENA) savings-related customer needs and behaviors, businesses can now add these saving tools to their own platforms to drive growth and loyalty, while also delivering value to their customers.
Cashbee
Cashbee, a French mobile application, has multiple savings solutions. Features include automated savings plans with user-determined amounts and frequency, a round-up option, and savings challenges based on setting and meeting targets and earning rewards. Setting goals enables users to track their progress, and cashback rewards are given on purchases made using the app at partner merchants. Cashback rewards can be automatically deposited into Cashbee savings accounts.
Raisin
German fintech company Raisin offers an online savings marketplace for customers across Europe. It currently manages more than €28 billion in assets. Raisin enables its “distribution bank” partners to offer their customers a range of third-party savings products from different banks across Europe. In addition, Raisin functions as a marketplace, partly under the brand name “WeltSparen,” where customers can compare and access a wide range of deposit products from banks across Europe. This platform also includes a variety of tools and resources to help customers make informed decisions about their savings, such as a savings calculator and access to expert advice.
Yolt
Yolt, a personal finance management app, offers several saving features that include round-up savings and goal setting and tracking. Its unique attributes include smart spending insights, which analyze spending habits and identify areas where users can save money, and a budgeting tracker for setting spending limits and managing finances effectively. Yolt also partners with savings providers to offer its users competitive interest rates on their savings, allowing them to easily compare and switch.
CONCLUSION
OPPORTUNITIES FOR ALL
Embedded savings is proving to be an effective approach for businesses that wish to introduce their customers to opportunities to increase their savings. This concept has the potential to transform the financial industry by providing individuals with new ways to save and invest and presenting businesses with new sources of revenue.
While embedded savings can be a great opportunity for businesses, it’s essential for them to ensure that their programs are transparent, comply with regulations, and protect the interests of all stakeholders. This includes the customers, retailers, banks, investors, and regulators.
Overall, embedded savings is a win-win situation for businesses and customers alike. By expanding to include these services, businesses can provide their customers with a better customer experience, increase customer loyalty, and earn revenue from new sources. Customers appreciate options to save money in a convenient and accessible way that could result in faster achievement of goals.
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, businesses have a unique opportunity to integrate embedded savings into their customer journeys and reap the accompanying benefits. It is time for businesses to make the most of this approach and share with their customers a new way to save and invest.
DOWNLOAD THE FULL REPORT
DATE

Executive Summary
AN UNDERESTIMATED RESOURCE
Embedded finance (EmFi) arguably has been the most hyped financial technology topic of the past two years. Its rise has forced traditional finance to take a back seat to make way for a more integrated and seamless customer experience. The EmFi market size and its many components, including payments, lending, savings, insurance, and investments, is estimated to reach US $7.2 trillion by 2026.
While EmFi’s focus is often on payments and lending, there is a lesser-known side of the trend: embedded savings. Despite the possibilities, which are wide-ranging and largely untapped, embedded savings has yet to receive its share of recognition and attention. In this Report, we aim to shed light on the importance of embedded savings and why it deserves more consideration in the context of EmFi. We will examine:
-
How embedded savings differs from other forms of EmFi.
-
Categories of embedded savings products.
-
Benefits of incorporating embedded savings into an EmFi strategy.
-
Real-life use cases that already exist around the world.
-
Criteria for selecting the ideal technology partner.
1
UNCOVERING THE POTENTIAL OF EMBEDDED SAVINGS
EmFi is essentially the placement of a financial product in a nonfinancial customer experience, journey, or platform (see Figure 1). This concept is transforming the way customers and businesses approach financial services (see Figure 2). The following EmFi components have already gained traction:
-
Embedded banking — the integration of banking services into nonfinancial products and services. This integration can take various forms, such as card issuance or “know your customer” (KYC) verification integrated into a mobile app or online platform.
-
Embedded payments — the integration of payment services into nonfinancial products and services. Enabling mobile payments within a ride-sharing app or allowing customers to pay for goods and services through a social media platform are two examples.
-
Embedded lending — the integration of lending services into nonfinancial products and services. Like embedded payments, this service can take different forms, such as financing options for products or services, or loans within a bundled package. For example, an automobile dealership may offer financing options for customers looking to purchase a car by including lending services in the dealership’s overall offerings.
-
Embedded wealth — the integration of wealth management services into nonfinancial products and services. This can be accomplished by providing access to investment options, retirement savings plans, and other financial products embedded as part of a broader offering. Wealth management firms aim to offer customers added convenience and value while expanding their revenue streams and reaching new markets.
-
Embedded insurance — the integration of insurance services within nonfinancial products and services. Adding insurance coverage to a product or service or offering insurance products as an additional benefit to customers are two of the many possibilities.
-
Embedded anything — the integration of financial tools for taxes, accounting, and invoicing into nonfinancial products and services. Examples include embedding tax-preparation services into accounting software or integrating invoicing services into an e-commerce platform.


One aspect of EmFi that remains relatively unexplored is embedded savings: the integration of savings and investment services within nonfinancial products and services. Embedded savings enables customers to easily save small amounts of money — or save and invest — as part of their everyday transactions. The concept of embedded savings is relatively new, and many people are not yet aware of its benefits and applications. Generally, the conversation around EmFi has largely centered on services that drive revenue and growth for businesses, like payments and lending, rather than savings, which promote financial wellness and stability for individuals. However, embedded savings has the potential to drive revenue and growth for the customer, embedder, and provider.
While the established elements of EmFi play a significant role in shaping the future of finance, embedded savings arguably has the most potential to meaningfully change the lives of customers and businesses by making it easier and more convenient to save for a rainy day, a specific future need, or long-term investments.
2
WHY TALK ABOUT EMBEDDED SAVINGS NOW?
Savings form a crucial foundation for financial activities, including lending, liquidity provision, and investment. A reduction in deposits and savings might force a bank to sell assets or seek other ways to create liquidity. Failing to attract deposits can have dire repercussions on the bottom line, as shown by the failure of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in March 2023. Banks do not always view savings as a core aspect of their business strategy, so they may not prioritize promoting this product. Instead, banks will prioritize lending and investment activities, which generate more revenue for them. Savings may be viewed as a peripheral activity that does not align with their primary objectives, and it may not generate enough revenue for banks to justify the cost of managing the accounts. As a result, banks may not be promoting savings as much as they could, even though these accounts are necessary to financial wellness and can help attract and retain customers.
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted many aspects of life, including individuals’ saving habits. The personal savings rate — how much money people save compared to their total disposable income — spiked during the pandemic. In 2020, according to Moody’s, the estimated personal savings rate in the US averaged 9%. This was attributed to several factors, including lower expenditures on items such as transport and entertainment, reduced opportunities to spend money due to lockdowns and other restrictions, and for some, additional income from government stimulus and support programs.
By October 2022, the surge in living costs and inflation rates that followed the pandemic quickly reversed the saving trend, causing a drop in the personal savings rate to 2.3% (see Figure 3). However, the rising inflation trend ended near-zero and sub-zero interest rates. The interest rates on savings accounts are tracking the base rates and rising for the first time since 2007–2008, with interest rates of 4%-5% becoming attainable in most localities. In March 2023, four different providers were offering rates over 4% in the UK, according to Bankrate.com.

As prices and interest rates payable on savings are rising, it is not surprising that people have become fussier about their banking products and are open to switching providers in the hopes of beating inflation through their savings. Meeting customers’ changing needs has increased demand for innovative solutions to help individuals save and manage their money. Embedded savings is flexible and adaptable, and it should be at the forefront as it offers unique, effective solutions for individuals to automate their savings and achieve their financial goals.
The climate is favorable for developing and launching embedded savings products thanks to both positive and negative undercurrents that impact individuals, businesses, and the world:
-
Changing consumer behavior. With a growing awareness of the importance of personal finance and saving, customers are seeking solutions that can help them achieve their financial goals with ease. Embedded savings can meet their needs by providing an effortless and automated way to save. It aligns with the idea of holistic wellness, which encompasses physical, mental, and financial well-being, by offering an easy and convenient way to improve one’s financial wellness without sacrificing time and energy.
-
Technology breakthroughs. The availability of infrastructure like banking as a service (BaaS) and open banking has enabled the seamless integration of savings into daily routines, including online shopping, mobile banking, and payments. This allows customers to save unconsciously and presents opportunities for businesses to embed finance solutions in their platforms, which makes saving more convenient and accessible for individuals. Open banking gives customers access to their banking information and services through third-party providers, enabling greater flexibility and choice. These technological advancements create new opportunities for businesses to offer embedded savings solutions and meet the growing demand for convenient savings options.
-
Untapped market potential. The rise of fintechs and new financial platforms has made it easier for customers to access financial products and services and enjoy better user experiences. These new entrants have successfully attracted large numbers of customers, including younger and tech-savvy ones. By integrating savings and investment options seamlessly into existing platforms, embedded savings solutions can provide a more holistic approach to financial management that is advantageous for customers, which can help drive mainstream adoption of these solutions and lead to a new era of financial wellness.
-
Economic volatility. Across the globe, the average 30-year-old has witnessed several major financial crises, including the 2008 housing bubble, the 2012 European debt crises, hyperinflation across developing world economies, and the crypto rise and crash. These economic fluctuations have left many customers feeling uncertain about their financial future. Embedded savings can address their concerns and impart a sense of stability by helping them save automatically, regardless of the state of the economy. Customers build a cushion for unpredictable times, maintain their purchasing power, and plan for the future with greater confidence.
-
Declining customer trust. In recent years, trust in traditional banks has been declining, and many customers are turning to alternative brands for their financial needs. For example, Apple has become a major player in the financial industry, starting with facilitation of payments through Apple Pay, followed by issuance of Apple Card with Goldman Sachs that incentivizes its users to transact and engage with the card, and most recently Apple rolled out high-yield savings accounts for its Apple Card users. According to FDIC data, more than 85% of US banks have less than $1 billion in total assets, which suggests that customers are increasingly seeking out nontraditional financial options. The shift in customer behavior presents both a challenge and an opportunity for traditional banks. Banks can maximize emerging solutions like embedded savings to meet the evolving needs of their customers and build long-term trust and loyalty.
These factors, along with the drivers shown in Figure 4, highlight why now is the perfect time for businesses to build solutions around embedded savings, which make it easier for individuals to achieve their financial goals.

3
EXPLORING THE COMPONENTS OF EMBEDDED SAVINGS
According to a report by the Financial Health Network, people who use automatic savings tools save on average $217 more per month (equivalent to 7% of an income of $3,500) than those who do not.
Because embedded savings continues to gain momentum, it is essential to understand its fundamentals. It encompasses a wide array of products and services, from traditional savings accounts to cutting-edge, micro-saving solutions that allow customers to regularly save small amounts of money. Let’s delve into the various types of embedded savings and micro-savings and highlight some of the industry leaders that have successfully implemented these state-of-the-art solutions:
-
Automated savings. This mechanism allows individuals to put money aside without having to actively think about it or make manual transfers. The basis is simple: make saving as effortless as possible. Automating the process may make customers less likely to change or cancel it, and more likely to stick to it. One example is Astra Finance, a US-based fintech, which allows its customers to set up automated transfers between their different accounts.
-
Round-up savings. This type of micro-saving rounds up transactions to the nearest whole unit and automatically transfers the difference into a savings account. Rounding up is designed to help individuals save small amounts of money regularly; they can accumulate a balance without even realizing it. It makes saving money effortless and convenient. Jar, a fintech based in India, offers its users the opportunity to round up their purchases and invest the amount in safe commodities such as gold.
-
Social savings. As the name suggests, this approach brings a group of individuals together to save toward a selected common financial goal, harnessing the power of community and peer pressure to encourage people to save more. By pooling their resources, individuals can achieve their financial goals more easily, as they are able to save more than they would be able to on their own. Nigerian fintech Cowrywise leverages the passion fans have for sports to encourage saving. Customers can use the Cowrywise platform to link their savings account to their favorite football team. Every time the team scores, Cowrywise automatically transfers a monetary incentive into the customer’s savings account.
-
Behavioral savings. This tactic leverages psychology and behavior-change theories to encourage customers to save more, using gamification, social comparison, and nudging strategies to help customers develop healthy savings habits and reach their financial goals. For example, US-based mobile app Qapital enables users to customize their savings using the If This Then That (IFTTT) rule. Users can identify specific behaviors, such as checking into a gym or buying coffee, and set up automated transfers for their accounts that are carried out in conjunction with those behaviors.
-
Save now, buy later (SNBL). This creative new model started in Africa and allows customers to save for desired items in small increments, optimize their cash flow, lock in deals, and avoid borrowing (i.e., buy now, pay later). An SNBL provider teams up with retailers to offer the service to the customer at checkout. As customers hit milestones on the way to saving for the item they want, they earn cash back and rewards from the retailer. FlexPay Technologies, Tunzaa Fintech, and CDcare offer SNBL.
The market is now witnessing the rise of specialized companies dedicated to seamlessly embedding solutions such as those described above into businesses’ journeys, providing customers with a new realm of opportunities to achieve financial stability and growth.
4
UNLOCKING THE BENEFITS OF MICRO-SAVING
As the trend of micro-saving gains momentum and the number of providers offering embedded savings solutions increases, it becomes evident that this field is ripe for imagination. Merging micro-saving with a business’s other offerings can improve the bottom line for both the business and the customers. Some potential benefits are:
-
Increased customer engagement. Offering micro-saving features can help to increase customer engagement and foster loyalty, as customers are able to save and manage their finances in a way that is convenient and incorporated into their daily lives.
-
Improved financial wellness. By providing customers with easy and convenient ways to save, businesses can help improve customers’ financial wellness and contribute to a more financially stable community.
-
Enhanced customer experience. Adding micro-saving features to a business’s products can create a more seamless and enjoyable customer experience and make it easier for customers to achieve their financial goals and feel more in control of their finances.
-
Increased brand differentiation. Offering options for micro-saving can set a business apart from its competitors and position it as a leader in financial innovation, which could attract new customers and increase brand recognition.
-
Increased revenue. Providing customers with a valuable service that supports their financial goals will benefit businesses as well by resulting in new revenue streams and increasing their customer base, and ultimately leading to increased profitability.
-
Improved financial literacy. Offering micro-saving features can help to improve financial literacy by showing customers the different ways they can harness their spending and encouraging them to make informed financial decisions, which can have a positive impact on their financial futures.
Now that we have a clear understanding of micro-saving, its various components, and the potential benefits it can bring businesses and customers, it’s time to explore the specifics of implementing a strategy.
A recent study from the UK found a significant increase in savings participation from the integration of automated savings into payroll, which soared from a mere 1.3% to an impressive 52.6%. This highlights the effectiveness of embedded savings in encouraging individuals to save and take control of their financial well-being. How can businesses effectively incorporate micro-saving into their offerings and maximize this innovative financial service for the benefit of their customers and their brand?
5
EMBEDDED SAVINGS USE CASES — FROM LUXURY GOODS TO UTILITIES
Here are several examples of how embedded savings and micro-savings can be folded into businesses across different industries:
-
Luxury goods. Many people are interested in purchasing luxury items, but it can be a challenging goal to achieve. Micro-saving offers a solution by enabling customers to set aside small amounts of money over time. For instance, a customer could decide to save for a luxury bag and have a designated amount automatically transferred into their savings account each month. This would increase the chance of success as saving would become a regular and automatic part of their routine.
-
Retail. Retailers can enhance customer loyalty and drive repeat business through a micro-savings program. For example, a clothing retailer can offer a program where customers can automatically set aside a small amount each time they make a purchase. This allows customers to save for a desired item and encourages them to continue shopping at that store. In this way, the micro-saving tool creates loyal, returning customers.
-
Travel. There are clear applications for the travel industry. Many individuals aspire to travel, but the expense is often too high. Travel companies can support their customers by providing micro-savings plans to fund their travel dreams. Implementing a program where a small amount is automatically saved from each purchase or booking can assist customers in saving for their future travels and benefit the travel company by boosting customer loyalty and generating repeat business.
-
Health and wellness. A health and wellness company can introduce a savings plan to encourage customers to lead healthier lifestyles through exercise and eating well by offering incentives for reaching predetermined objectives. This assists customers in saving during their journey toward their health and wellness goals while reinforcing positive habits, leading to a healthier lifestyle. To enhance customer engagement, a gym could implement a savings program that rewards members who meet their fitness goals and penalizes those who don’t by adjusting the interest or reward paid into the savings account based on a customer’s behaviors.
-
Home and car ownership. Real estate companies can provide a savings program aimed at helping customers accumulate funds for a down payment. This program can be seamlessly integrated with the company’s other services, such as mortgage brokerage or property management, to support customers in achieving their homeownership aspirations. Car dealerships can offer similar programs for customers who wish to save for a car purchase by integrating their financing and insurance services. In such scenarios, customers could be offered discounts in buying the adjacent services (i.e., insurance and services) if the payment toward those services is made through the savings program. This not only supports customers in reaching their goals but also strengthens customer loyalty, increases customer conversion, allows the business to close more sales, and prevents the loss of potential customers.
-
Retirement savings. Financial services and insurance companies can offer micro-savings plans for retirement saving. The plan could be integrated into the company’s existing products, such as investment services, and would facilitate saving small amounts and managing retirement funds over time. By automating the process, customers can consistently contribute to their retirement savings goals and gradually grow their nest egg. The convenience and simplicity of this micro-savings plan can encourage customers to prioritize retirement saving and achieve their financial goals.
-
Energy and utilities. A utility provider can encourage customers to reduce their energy consumption by introducing a micro-savings feature. Whenever the customer saves energy — through using energy-efficient appliances or turning off unneeded lights, for example — the provider will automatically place the difference between the energy saved and their average usage into a savings account. This creates a tangible incentive for customers to conserve energy; they will see their savings grow with each effort to reduce their energy usage. The utility provider benefits as well, as it can reduce the demand for energy and lower its costs. The provider can also earn revenue from the program, creating a mutually beneficial solution for both parties.
These are just a few examples of how micro-saving can be incorporated into different businesses to improve customer engagement, enhance the customer experience, and achieve specific financial goals for businesses and individuals.
6
CHOOSING THE RIGHT TECHNOLOGY PARTNER
An embedded savings program can help a business support its objectives while significantly contributing to its customers’ financial wellness and stability. The right technology partner can offer customization options tailored to the business’s unique requirements and oversee a smooth and successful implementation. To ensure compatibility between a business and a technology partner, look for a partner that offers the following features:
-
Automated customer savings. Essential to any embedded savings program, this feature streamlines the savings process for customers, making it effortless and stress-free. By automating, a business can help its customers keep track of their financial progress and empower them to achieve their financial goals. These include recurrent savings, round-up savings, behavioral savings, and others.
-
Regulation-compliant value storage. It is crucial to ensure that the stored value, which is the balance needed for future transactions, complies with relevant regulations to protect the customers’ savings. This ensures the security and protection of their funds, which helps build trust in the business and enhances the overall customer experience. A deep understanding of the regulations for issuing stored value is critical to effectively operate any embedded savings program and provide peace of mind for customers.
-
Goal-based savings. This option helps customers envision their objectives and build their savings accordingly by enabling them to set a target and track their progress. Customers gain a clear vision of their financial future, which keeps them motivated to save.
-
Bank accounts with data integration. A comprehensive view of a customer’s financial situation and spending habits is essential for effective savings. Bank accounts with data integration offer valuable insights into customer finances. This integration supports informed financial decision-making and drives additional savings to help customers reach their financial goals while giving the business a better understanding of its customers and their financial needs.
Embedded savings is starting to gain more relevance and popularity as more fintechs shift their focus to this underutilized segment of EmFi, and businesses are taking note of the results. This is a good time for businesses to exploit the developing interest in and options for embedded savings to seek out the right partnership.
By collaborating with a fintech provider that offers the features it needs, a business can ensure that its embedded savings program is effective, efficient, and customer-centric. A strong collaboration supports the business’s goals and promotes financial wellness and stability for its customers.
There are several fintechs helping businesses develop their ideal embeddable saving programs; these include global companies like Meniga, Dreams Technology, and regional players like Coinscrap in Spain and TWIG in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). Each offers comprehensive platforms that provide what is needed to implement an effective embedded savings program. The accompanying case studies represent trailblazing ideas that utilize EmFi to bring value and revenue to the fintech industry.
Case studies
Acorns
Acorns is an Irvine, California, USA-based fintech founded in 2012. The company offers a mobile app that enables users to invest their spare change from everyday purchases into a diversified portfolio of exchange-traded funds (ETFs). The company’s unique approach to savings has been a game changer in the financial industry, allowing people to invest small increments with ease. With over 8 million users, Acorns has gained significant recognition for its innovative platform, which also includes personalized investment advice, retirement savings accounts, and educational tools to help users manage their finances effectively.
Qapital
Qapital is headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, and operates in the US and Canada. The company was founded in 2012 by a group of financial and technology experts whose goal was to provide a mobile-based platform to help people save money more easily. Qapital has earned attention for its creative approach to savings. Its mobile app offers unique tools designed to help users personalize their experience, like the “Rules” feature, which guides the creation of behavior-based savings criteria, including the use of IFTTT, which work automatically to save money based on specific actions or events.
N26
N26 is a fintech company operating in Europe and the US. Founded in 2013, it provides mobile-based banking services with a user-centered approach to design. Its commitment to providing modern and convenient banking services has made it a popular choice for customers looking for a hassle-free banking experience. N26 offers various saving automations embedded in its application, such as automated transfers between accounts, with a feature that rounds each transaction up to the nearest euro or dollar and automatically saves the difference. N26’s features make saving a seamless part of everyday life, helping users achieve their financial goals.
Jar
Founded in 2021, Jar is a fintech company operating in India. Jar provides a mobile-based savings platform that enables users to link their bank accounts and automatically invest spare change from each transaction in gold. Saving through gold investing is an attractive option for people looking to diversify their investment portfolio and protect their savings against market fluctuations. By offering a savings solution that allows users to invest in gold, Jar is tapping into a cultural preference and providing a convenient way for people to invest in this valuable asset.
TWIG
TWIG is a UAE-based fintech founded in 2021. Originally a direct-to-customer mobile app, TWIG’s platform offers micro-saving functionalities to drive additional savings such as rounding up, goal-based savings, and artificial intelligence (AI)-based budgeting. The company’s product-driven approach prioritizes customer and user experience. With its expansion to include B2B2C solutions and its deep understanding of the Middle East and North Africa’s (MENA) savings-related customer needs and behaviors, businesses can now add these saving tools to their own platforms to drive growth and loyalty, while also delivering value to their customers.
Cashbee
Cashbee, a French mobile application, has multiple savings solutions. Features include automated savings plans with user-determined amounts and frequency, a round-up option, and savings challenges based on setting and meeting targets and earning rewards. Setting goals enables users to track their progress, and cashback rewards are given on purchases made using the app at partner merchants. Cashback rewards can be automatically deposited into Cashbee savings accounts.
Raisin
German fintech company Raisin offers an online savings marketplace for customers across Europe. It currently manages more than €28 billion in assets. Raisin enables its “distribution bank” partners to offer their customers a range of third-party savings products from different banks across Europe. In addition, Raisin functions as a marketplace, partly under the brand name “WeltSparen,” where customers can compare and access a wide range of deposit products from banks across Europe. This platform also includes a variety of tools and resources to help customers make informed decisions about their savings, such as a savings calculator and access to expert advice.
Yolt
Yolt, a personal finance management app, offers several saving features that include round-up savings and goal setting and tracking. Its unique attributes include smart spending insights, which analyze spending habits and identify areas where users can save money, and a budgeting tracker for setting spending limits and managing finances effectively. Yolt also partners with savings providers to offer its users competitive interest rates on their savings, allowing them to easily compare and switch.
CONCLUSION
OPPORTUNITIES FOR ALL
Embedded savings is proving to be an effective approach for businesses that wish to introduce their customers to opportunities to increase their savings. This concept has the potential to transform the financial industry by providing individuals with new ways to save and invest and presenting businesses with new sources of revenue.
While embedded savings can be a great opportunity for businesses, it’s essential for them to ensure that their programs are transparent, comply with regulations, and protect the interests of all stakeholders. This includes the customers, retailers, banks, investors, and regulators.
Overall, embedded savings is a win-win situation for businesses and customers alike. By expanding to include these services, businesses can provide their customers with a better customer experience, increase customer loyalty, and earn revenue from new sources. Customers appreciate options to save money in a convenient and accessible way that could result in faster achievement of goals.
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, businesses have a unique opportunity to integrate embedded savings into their customer journeys and reap the accompanying benefits. It is time for businesses to make the most of this approach and share with their customers a new way to save and invest.
DOWNLOAD THE FULL REPORT